Of three modes of heat transfer – Conduction, Convection & Radiation – the least understood is mode is Radiation, especially with regard to human thermal comfort. Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted from the surface of a body as a result of its temperature. The picture below shows three modes of heat transfer:
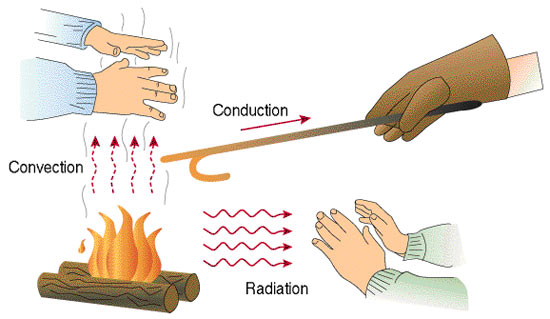
As can be seen from the above diagram, Radiation does not require any medium unlike Conduction and Convection.
Radiant Cooling is based on the physical principle that bodies with varying temperatures exchange thermal radiation until an equilibrium is achieved. The principle of Radiant Cooling has been around in nature and human beings have using this principle knowingly or unknowingly for ages:
- Inner walls of the caves are at a lower temperature as the heat from solar radiation does not percolate down to these walls. In addition, these walls are cooled due to the water streams, vegetation etc.
- Snow-packed walls in buildings in 8th century Mesopotamia
- Lotus Mahal in Hampi has intricate channels along the walls through which water flowed to take away the heat from the interior.
Modern Radiant Cooling follows the same principle to cool a floor or ceiling (or even walls) by absorbing heat radiated by the rest of the room. As can be seen in the diagram below, a Cooled Ceiling acts as a heat sink for all radiant heat sources in the room (human occupant, solar radiation, equipment, walls etc.).
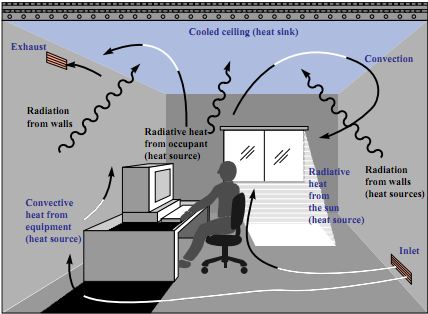
Note that Radiant Cooling is not a “high side” system that replaces Chiller. Radiant Cooling is a “Low Side” technology that relies on chilled water pipes to distribute cooling throughout a building rather than using chilled air and ductwork.
Radiant cooling systems rely mainly on the direct cooling of occupants by radiative heat transfer because the pipes, which are commonly run through ceilings, maintain the surface at temperatures of about 20-22 deg C. Through radiative heat transfer, people in the room will emit heat that is absorbed by the radiant cooling surface.
To manage indoor humidity levels and air quality, a separate ventilation system to supply fresh air is needed. Zoning of building can also be done due to ease of controlling flow of water.
Click here to know how Radiant Cooling works?
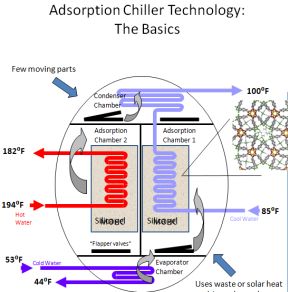 Adsorption Chiller
Adsorption Chiller
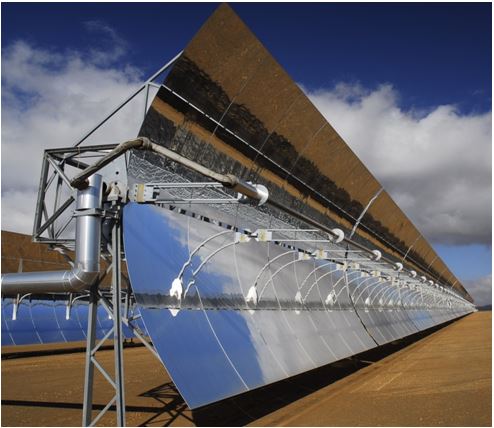 Large Aperture Parabolic Trough Concentrator (PTC72)
Large Aperture Parabolic Trough Concentrator (PTC72)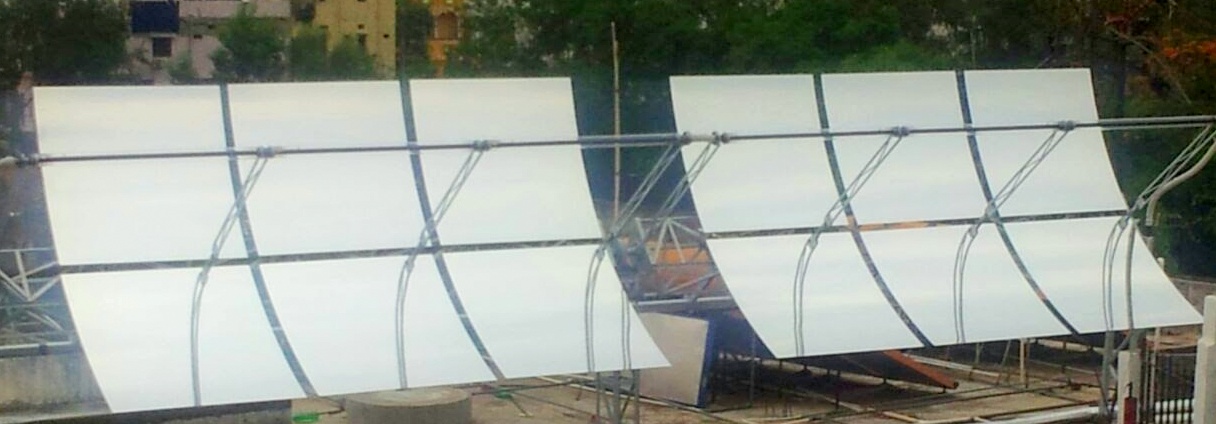 Rooftop Parabolic Trough Concentrator
Rooftop Parabolic Trough Concentrator
