Scope
The following processes in automobile manufacturing have scope for integrating solar heating:
- Phosphating Process
- Parts Washing
- Paint Shop Drying
- Sludge Drying
- Effluent treatment
Solar Integration for Phosphating
Phosphating process is used as a pretreatment method in conjunction with another method for corrosion protection. Phosphate coating is usually applied to the components by immersing them in solution baths as shown below:

Such baths use electrical heaters or diesel/furnace oil fueled boiler for maintaining the bath temperature around 90 deg C. Concentrating Solar Thermal (CST) technologies can be used to provide the heat required for phosphating process without any change to the process.
Parts Washing using Solar Heat
Parts washer is used to remove contaminants or debris such as dirt, grime, metal chips etc. from the components before they are assembled. These washing machines today used electrical heaters to raise the temperature of the water being used for washing.
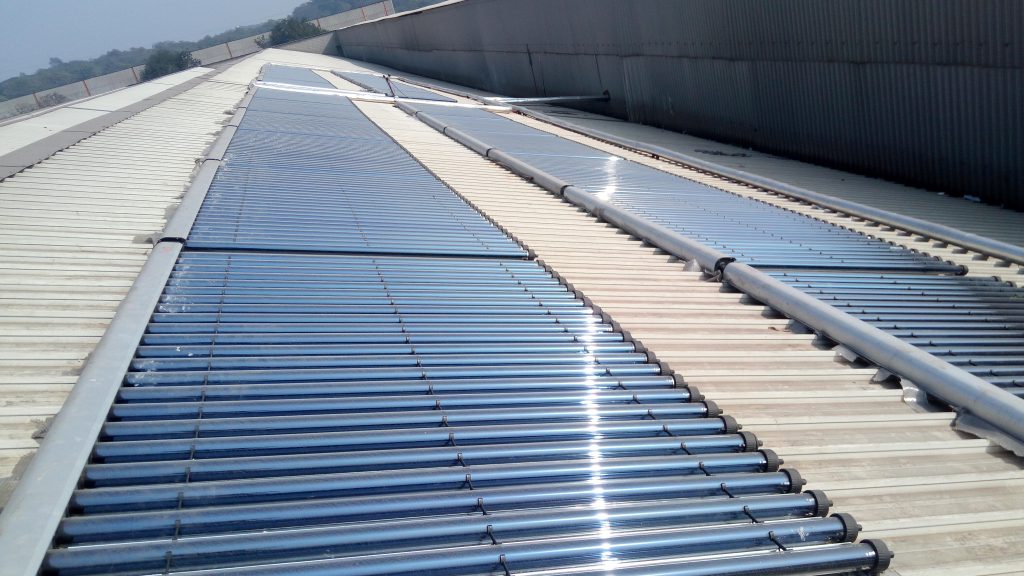

The temperature of the water is between 70-90 deg C and this can be provided by Compound Parabolic Collector (CPC) shown above. CPCs can be installed even on the shed roof. Solar heat can also be used during non-solar hours by incorporating hot water storage tank.
CPCs provide low concentration that is suitable for providing pressurized hot water upto 120 deg C. They do not require tracking and can utilize even diffuse radiation from sun. The maintenance requirements are also low and hence, are appropriate for low grade heat requirements (70-120 deg C).
Solar Paint Shop Drying
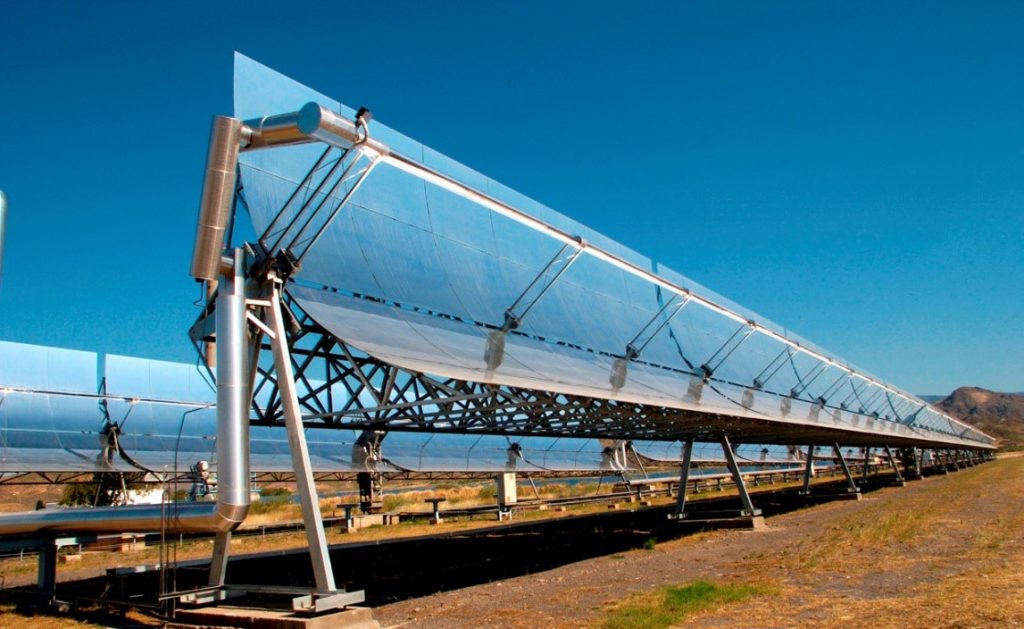
Paint shop is used for many automobile components, machine components and other made gadgets use paint shop for resistance against exposure to element of nature like chemicals, moisture, rain, dust, and for having an aesthetically appealing product. Paint curing requires heat, mostly in the form of hot air. Today fossil fuel based heating is used in paint shops, to generate curing air temperatures ranging from 80° C to 150° C. Atmospheric air being taken in by the oven can be fed with air pre-heating using solar concentrators.
CPCs or Parabolic Trough Concentrators (PTC) as shown below can be used for such requirements with a suitable thermic fluid to air heat exchanger.

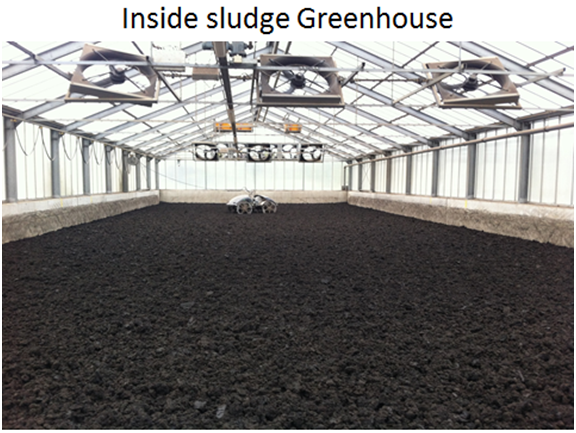
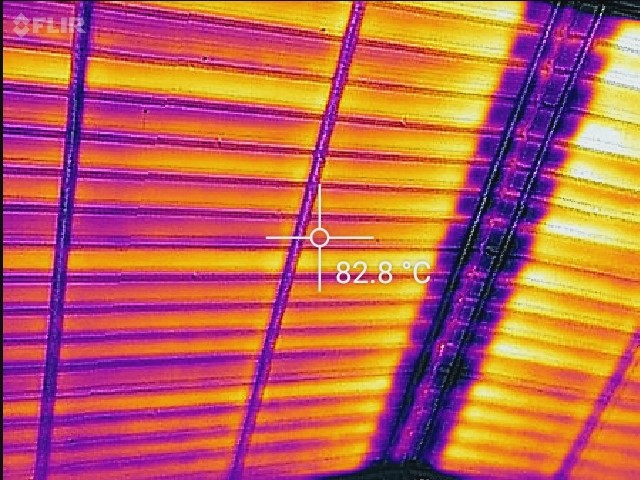
Solar Sludge Drying
Waste water sludge needs to be dried to minimize the its mass to reduce the sludge hauling and disposal costs. Today most industries dry sludge using open evaporation method. However, this process can be significantly accelerated by using solar heat in different forms.
Oorja integrates its expertise in Radiant Heating systems and Heat Pumps to design and implement a sludge drying system that further enhances the rate of drying of the sludge.
Solar Effluent Treatment
Many companies are now adopting Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) policy for treatment of effluents and a Multi Effect Evaporator (MEE) is generally being used to treat waste water and reuse it for process or other plant needs. MEE requires steam temperature of which is dependent on the number of stages of the evaporator. Today the MEE uses fossil fuels like diesel or natural gas or furnace oil.
Solar Concentrators can provide steam required for MEE to waste water treatment.
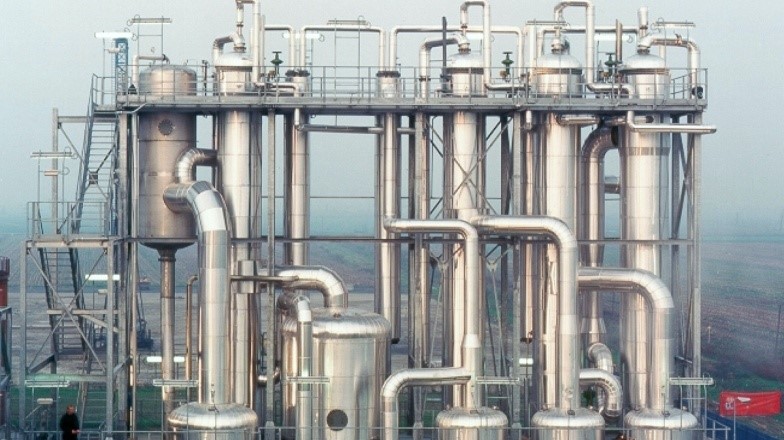

The solar field can be integrated with the existing boiler to operate the system in a hybrid manner. Oorja can provide all required engineering for integration of existing boiler with solar concentrator field.
About Oorja Energy Engineering
Oorja Energy Engineering is a complete Cleantech Heating & Cooling solutions company. We offer energy efficient and renewables based products and solutions for industrial and commercial heating and cooling requirements.
Oorja is a Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) approved manufacturer of Concentrating Solar Thermal (CST) systems. We can design & implement cleantech heating and cooling solutions for your specific requirements.








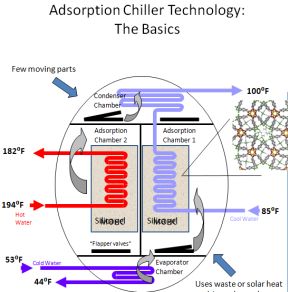 Adsorption Chiller
Adsorption Chiller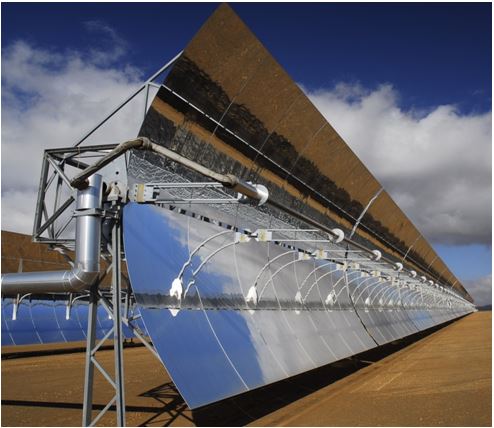 Large Aperture Parabolic Trough Concentrator (PTC72)
Large Aperture Parabolic Trough Concentrator (PTC72)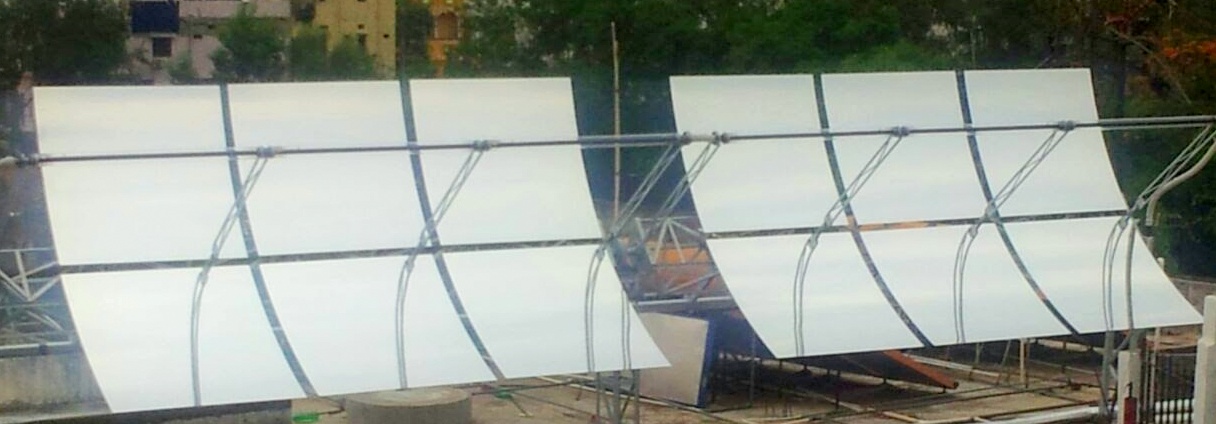 Rooftop Parabolic Trough Concentrator
Rooftop Parabolic Trough Concentrator